
Symptoms of a cyst that is not infected include: But a large cyst or an infected cyst (abscess) can cause symptoms. You may not have any symptoms if the Bartholin gland cyst is small. You can lower your risk of STIs by using a condom when you have sex. Infected Bartholin cysts are sometimes caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The cyst can get bigger after sex, because the glands make more fluid during sex. Things like thick mucus or swelling can block a Bartholin gland duct and cause a cyst. If the cyst is infected, you will need treatment. But if you have symptoms, you might want treatment. If the Bartholin gland or duct gets infected, it's called a Bartholin gland abscess.īartholin gland cysts are often small and painless. (Sometimes it's called a Bartholin duct cyst.) These cysts can range in size from a pea to a large marble. The blocked gland is called a Bartholin gland cyst. If a Bartholin duct gets blocked, fluid builds up in the gland. This fluid comes out of two tiny tubes next to the opening of the vagina. The Bartholin glands make a small amount of fluid to lubricate the vagina and the vulva. Most of the time, you can't feel or see these glands. The Bartholin glands are two small organs that are located on each side of the vaginal opening.
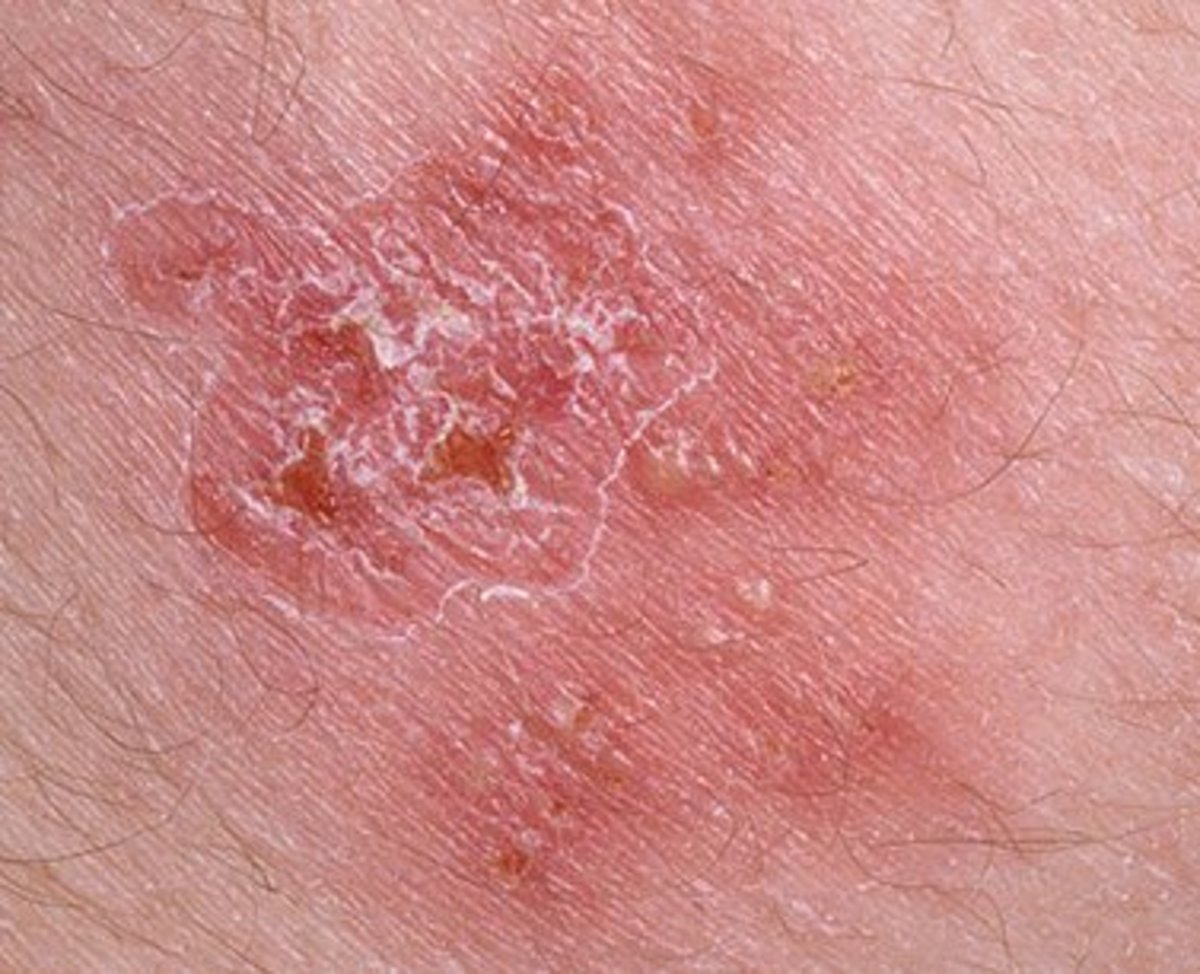
Soreness and a red, scaly area are symptoms of Paget disease of the vulva.Condition Basics What is a Bartholin gland cyst? Bartholin glands More often, however, a lump in this area is from a Bartholin gland cyst, which is much more common (and is not a cancer). Bartholin gland cancerĪ distinct mass (lump) on either side of the opening to the vagina can be the sign of a Bartholin gland carcinoma. If you have a mole that has changed, ask your doctor to check it out. Still, not all melanomas fit the ABCDE rule. The most important sign of melanoma is a change in size, shape, or color of a mole. There may be differing shades of tan, brown, or black and sometimes patches of red, blue, or white.ĭiameter: The mole is wider than 6 mm (about 1/4 inch).Įvolving: The mole is changing in size, shape, or color. The ABCDE rule can be used to help tell a normal mole from one that could be melanoma.Īsymmetry: One-half of the mole does not match the other.īorder irregularity: The edges of the mole are ragged or notched.Ĭolor: The color over the mole is not the same. Vulvar melanomas can sometimes start in a mole, so a change in a mole that has been present for years can also indicate melanoma. They can be found throughout the vulva, but most are in the area around the clitoris or on the labia majora or minora. Most vulvar melanomas are black or dark brown, but they can be white, pink, red, or other colors.

Patients with vulvar melanoma can have many of the same symptoms as other vulvar cancers, such as: Still, if you have these symptoms, you should have them checked by a doctor or nurse. These symptoms are more often caused by other, non-cancerous conditions. Verrucous carcinoma, a subtype of invasive squamous cell vulvar cancer, looks like cauliflower-like growths similar to genital warts.
SWOLLEN BUMP ON VAGINA SKIN
An area on the vulva that looks different from normal – it could be lighter or darker than the normal skin around it, or look red or pink.Invasive squamous cell cancer of the vulvaĪlmost all women with invasive vulvar cancers will have symptoms. Sometimes doctors might not even recognize the condition at first. Some try to treat the problem themselves with over-the-counter remedies.

However, an area of VIN can also appear red, pink, or darker than the surrounding skin.īecause these changes are often caused by other conditions that are not pre-cancerous, some women don't realize that they might have a serious condition. It is often thicker and lighter than the normal skin around it. An area of VIN may look different from normal vulvar skin. When a woman with VIN does have a symptom, it is most often itching that does not go away or get better. Most women with vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) have no symptoms at all. Symptoms depend on whether it is a cancer or pre-cancer and what kind of vulvar cancer it is.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
